Solar Inverter Efficiency
- Posted by Neo Messtechnik
- On 22. June 2023
- 0 Comments
Solar inverters with high voltage, large current, and high power are becoming increasingly common. This is done to increase power generation efficiency and reduce installation costs. This article introduces measurement of high voltages, large currents, and high power values when evaluating solar inverter efficiency.
Solar inverters play a crucial role in converting electrical energy for various applications. For example, they convert DC power from solar panels into AC power for the electrical grid. However, this conversion process results in energy loss, making the efficiency of solar inverters an important performance indicator. Efficient inverters effectively utilize generated electrical energy with minimal losses.

Table of Contents
PQA8000H – AC/DC Efficiency Analysis
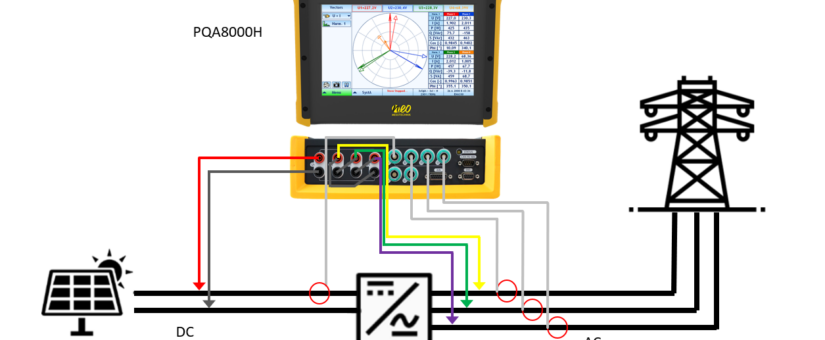
To accurately evaluate efficiency, the NEO Messtechniks PQA8000H is an excellent tool. This advanced instrument offers powerful calculation functionality for precise power analysis. By simultaneously capturing voltage and current readings from multiple points in a circuit, it enables comprehensive analysis of power components.
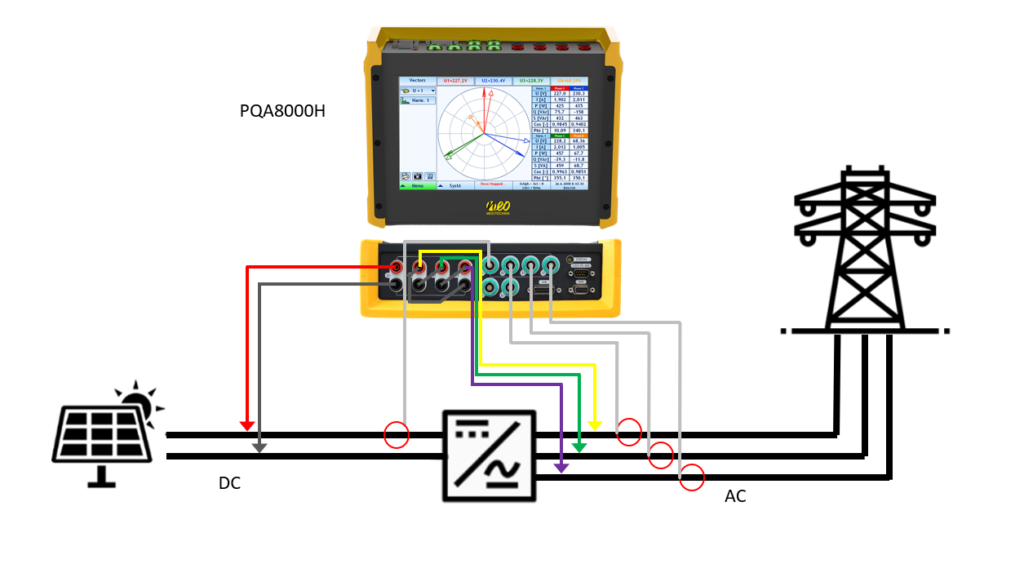
When it comes to current measurement, two common methods are used: current sensors and direct wiring. While direct wiring is challenging for measuring large currents, current sensors provide precise and accurate measurements.
For measuring high voltages, such as those exceeding 1000 V, a power quality analyzer employs various techniques like high-voltage differential probes, voltage transformers (VT, PT), or high-voltage dividers. Voltage transformers are unsuitable for measuring DC or waveforms like PWM, while high-voltage differential probes can introduce measurement errors. In contrast, high-voltage dividers offer precise detection capabilities for both DC and various waveforms like PWM, enabling accurate assessment of efficiency improvements.
Accurate assessment of power loss in a reactor requires measuring not only DC and the standard commercial line frequency (50 Hz/60 Hz) but also harmonic components. Switching frequencies and harmonics resulting from switching control can impact power input and output in a smoothing DC reactor.
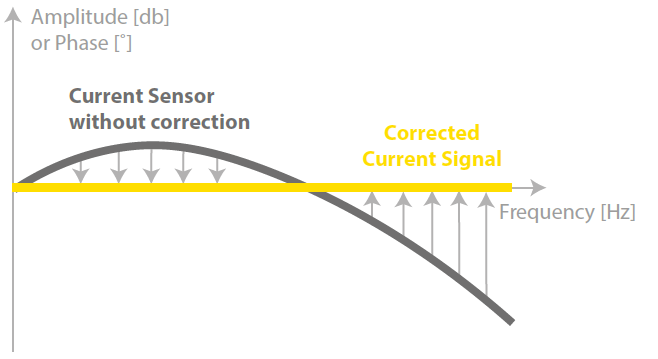
Current Sensor Correction
Instruments have their unique frequency characteristics, including fluctuations in amplitude error and phase error within the harmonic band. To ensure accurate measurement of power with diverse frequency components, it’s crucial to evaluate errors across the harmonic band, in addition to representative points like DC and the commercial line frequency. With this correction you can perform solar inverter efficiency measurements.
Wrapping up
Where can I get more information?