
DC Components in AC Grids
- Posted by Neo Messtechnik
- On 1. August 2023
- 0 Comments
In recent years, power quality measurements in the industry and in distribution and transmission networks have been carried out more frequently. During these measurements, the focus has been on classic parameters such as voltage sags, voltage transients, and harmonics. Maximum values are provided by standards for the quality of distribution networks, including:
- EN 50160
- IEEE 519
- Directive G5/4
- D-A-CH-CZ – Technical regulations for assessing network interactions
Moreover, the compatibility between distribution networks and products can be evaluated according to the standards IEC 61000-2-2 for public low-voltage networks and IEC 61000-2-4 for low-voltage and medium-voltage industrial installations. However, these standards have not explicitly included the power quality parameter DC offset (DC components).
Table of Contents
DC Limits in Standardization
In Germany, the DC component is addressed in the Technical Installation Guideline (TAR) for low-voltage since 2019 under section 5.4.4.9 “Injection of Direct Current into the Low-Voltage Network.” So, the guideline specifies the following: An inverter must not inject more than 0.5% of its rated current or a maximum of 20 mA (whichever value is higher) as direct current.
Note 1: The measurement of direct currents is performed based on DIN EN 61000-4-7 (VDE 0847-4-7) over 10 fundamental waveform periods.
Note 2: Direct currents can lead to corrosion damage to cables and other equipment, as well as transformer and other inductor saturation.
The standard explicitly lists inverters as undesirable sources of DC. Maximum values for the DC component can also be found in other countries. Three examples are listed in the table below.
| Country | Standard | Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Australia | AS4777.2 | 5 mA or 0.5% of the rated output current |
| USA | IEEE Standard 1547-2018 | 0.5% of the rated output current |
| Italy | CEI 0-21 | 0.5% of the rated output current |
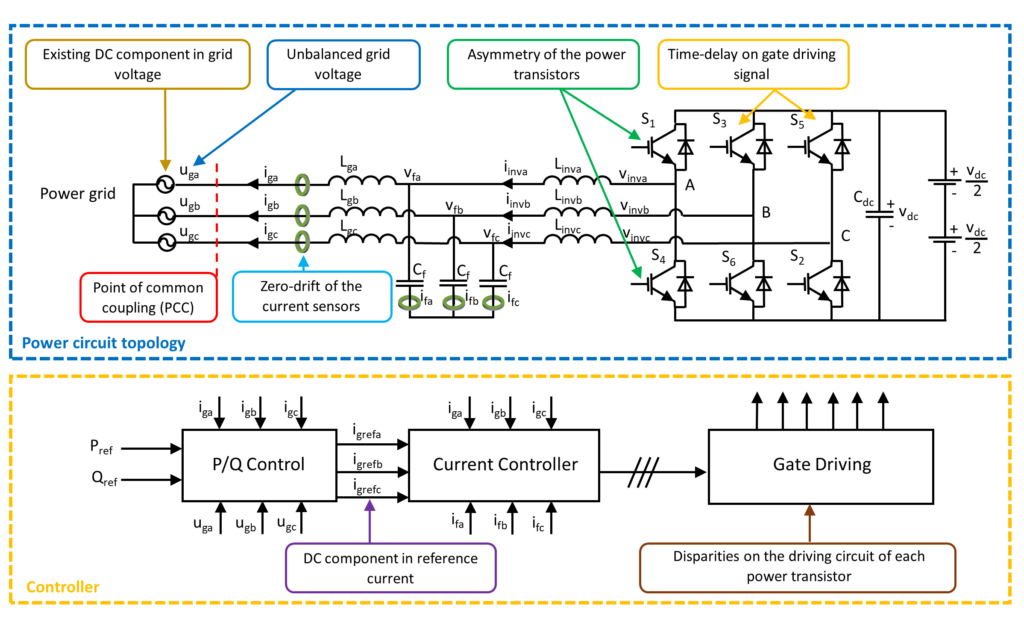
DC Sources of an Inverter
The potential DC sources in inverters are quite diverse, as illustrated in the following diagram of an inverter system.
Measurement system
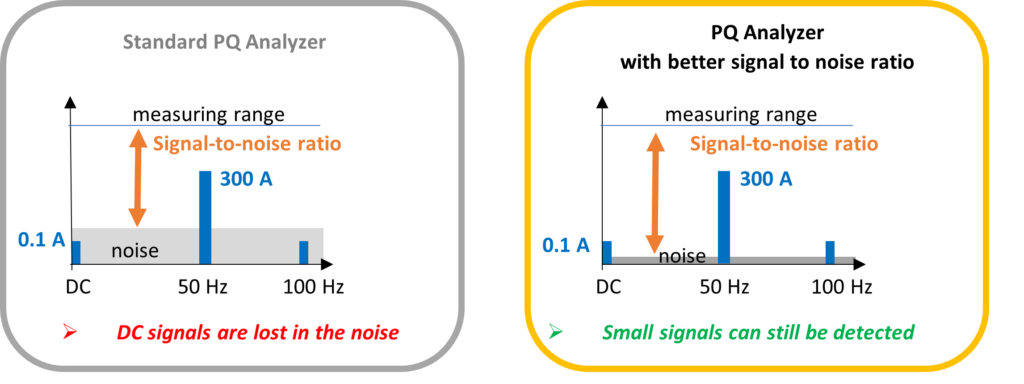
To measure small DC parts accurately, use a PQ device with strong signal quality. Noise may hide lower or higher levels at different frequencies. The device should compensate for DC offset in current sensors for precise measurements.
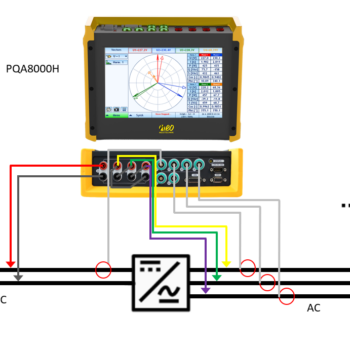
The Power Quality Analyzer PQA8000H by Neo Messtechnik connects to zero-flux transducers and lets you freely choose FFT analysis frequency parameters.

However, the standard grouping in IEC 61000-4-7 might be too coarse for low-frequency analysis. Still, the analyzer can detect geomagnetically induced quasi-DC currents (0-1 Hz) in high-voltage networks.
Conclusion
The inverter technology used in renewable energy sources is not only a potential source of harmonics. In recent years, there have been increasing reports that DC injection occurs in many cases as well. Non-linear loads, in addition to inverters, can also generate a DC component. Inductive equipment like motors and transformers are currently not designed to handle these loads. Despite efforts by inverter manufacturers to minimize the DC component, power quality measurements in low-voltage networks using AC/DC sensors often detect a significant DC component.
Check out the entire article in the PSD Europe September 2023 magazine (starting on page 41).
powersystemsdesign.com/print-archives-emb/588
Wrapping up
Where can I get more information?



0 Comments