Q&A – 12 answers to 10 questions in Chapter 6
- Posted by Neo Messtechnik
- On 13. April 2021
- 0 Comments
As we are closing the first section with a Power Quality Q&A, we are touching on further classic analyses and inside knowledge to complete the picture of classic power quality knowledge.
Table of Contents
– Overview
Welcome to Chapter 6 of our Multipart-Series
The list of previous articles has slowly but surely gained an impressive length. Here is everything you might have missed if this was your first drop into Power Quality Explained. To mix things up a little bit we decided to design this article as Q&A.
- Power Quality Analysis – A Reintroduction
- Foundational Knowledge
- Electric Power & Energy
- IEEE 519 & Harmonics
- Flicker, RVC & Symmetrical Components
- The Ultimate Guide to Power Quality 2021
- EN 50160
What do star-, delta- and single-line wiring mean?
The following table shows the relation of star and delta parameters, making it straight forward to easily calculate the respective values.
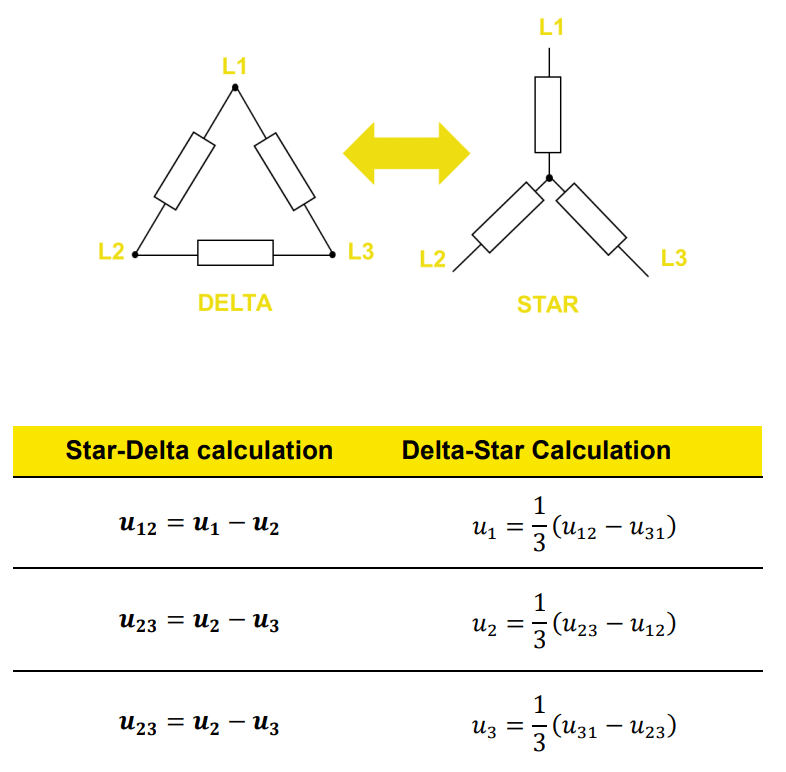
Star connection
Delta connection
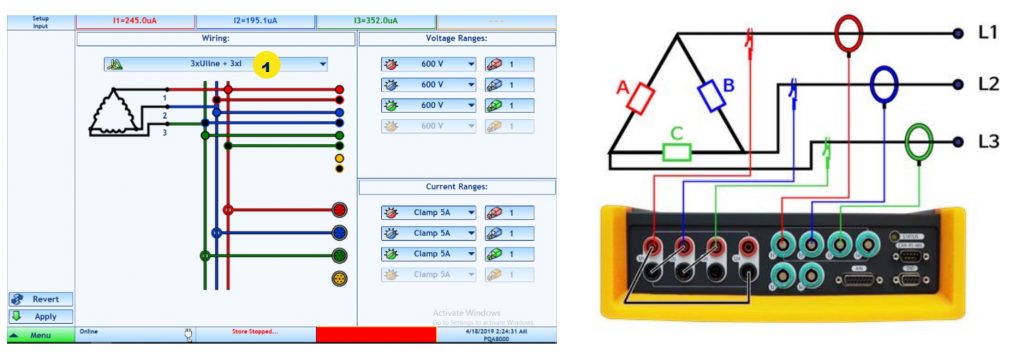
Single Phase connection
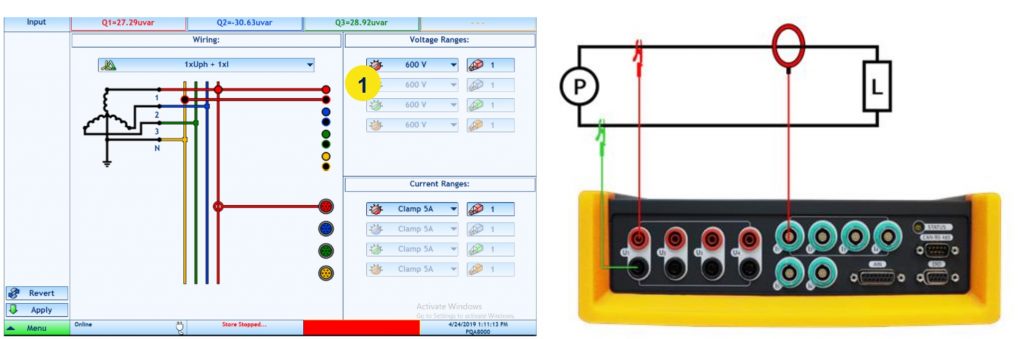
What does a Transient Recorder do?
A transient recorder detects any kind of waveform deviation from the ideal pure sine wave. Various trigger options allow triggering on input voltage or current signals, calculated software values (P,Q,S, THD, xth Harmonic etc.) and dynamic signal analysis (1/2 Period values, phase angle jumps, RoCoF, envelope trigger). Using NEO Messtechnik devices allows to combine multiple triggers as well.
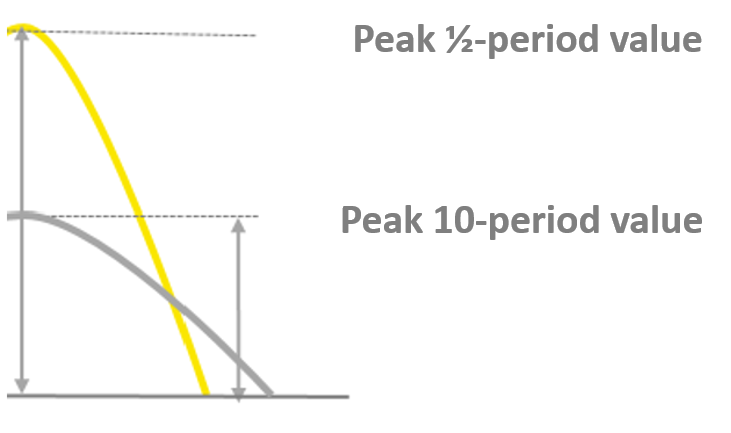
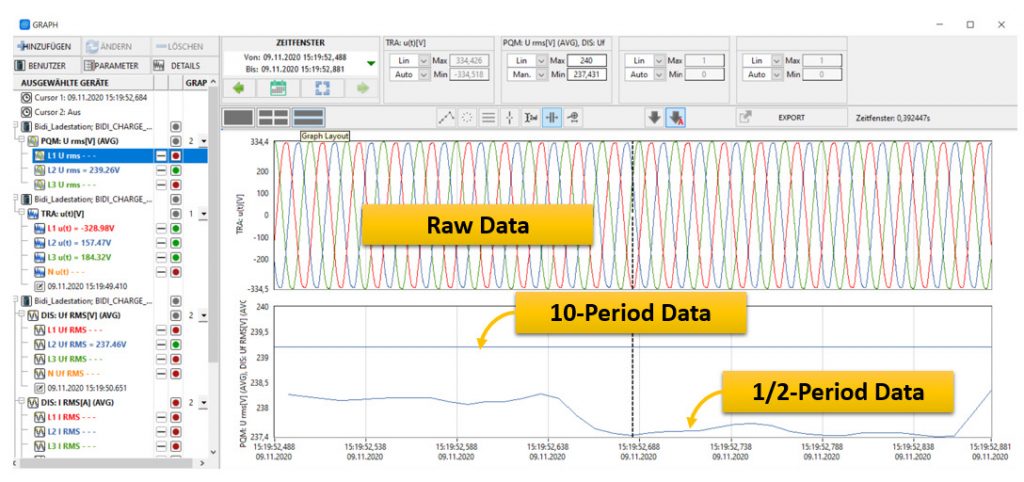
What are ½ period values?
½ period values make short-time interruptions visible. 10-period values, e.g. for the EN 50160, only show a dampened peak value of disturbances. The peak of ½ period values (real value) can be a couple of times higher than the measured 10-period value. It is a very important tool your power quality management solution should offer! For example, we offer our customers to store half-period values of U,I,P,Q,S, phi, symmetrical components, fundamentals and many more.
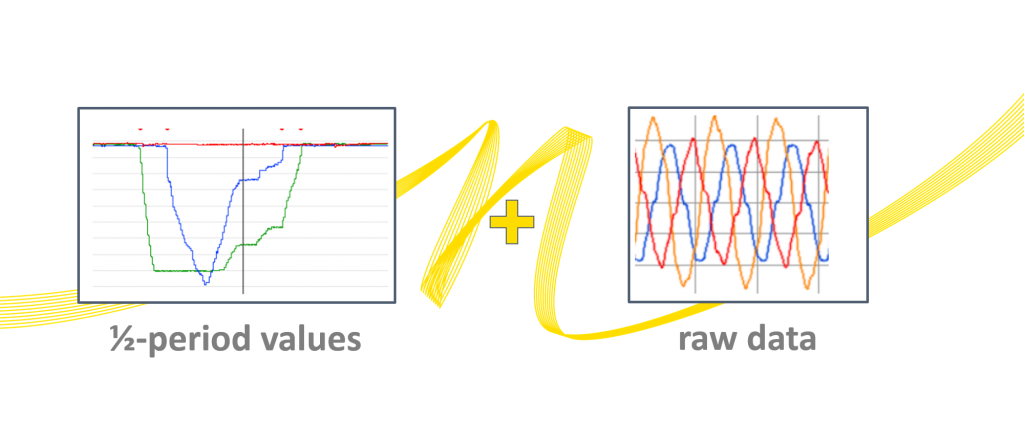
What is the difference between disturbance and transient recording?
Disturbance recording decreases the amount of data the user has to store over a longer time interval. This goes hand in hand with a loss of information about single samples and slightly restricts off-line analysis possibilities. However, for many power grid disturbances it will show the necessary information to identify the disturbance and the cause.
In contrast, certain grid situations like switching operations or resonances can only be analyzed in detail when there is raw sampling data (Transient record) available. As you might already guess, using both storing options combines their benefits and allows recording any kind of disturbance or waveform deviation in the grid, while using optimized data storage. The computer-based systems of NEO Messtechnik allows recording a high number of transients and disturbances with long recording time.
What is meant by system dynamics?
Under system dynamics we understand the appearance of phase angle jumps, variable frequency (RoCoF), dips or swells of the supply voltage or switching transients. These phenomena increasingly occur during the connection and reconnection of microgrids and distributed generator units (DER) and result in a higher system dynamics and growing interactions. Furthermore the power electronics development will stress the importance of measuring and analysing resonances, oscillations and the grid impedance itself.
What is the function of a PMU?
A Phasor Measurement Unit or PMU is a device for accurate synchrophasor measurements. When comparing the fundamental harmonics’s phase angle, measured at different points in the network, the difference serves for stating the status of the electric grid. In order to carry out this measurement you need several synchronized devices across various locations of the grid.
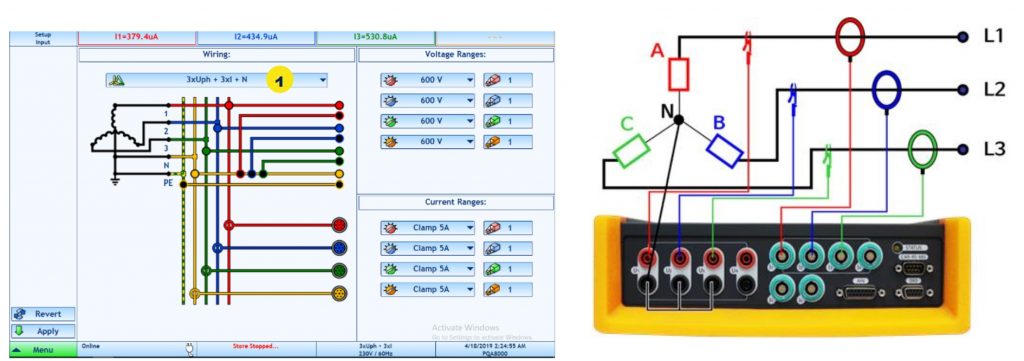
Could you explain the PMU IEEE C 37.118 standard?
The IEEE C37.118 defines the PMU accuracy in stabilized state and a communication protocol for real-time phasor transmission. Taking our PQA 8000 H as example that fully complies with the standard, it offers a built-in GPS receiver together with highly-accurate voltage inputs and
– Total Vector Error 0.01% (typ.)
– Angle Accuracy 0.003° (typ.)
The PMU firmware measures voltage and current phasors, frequency, and calculates the positive symmetrical components of voltages and currents. The measured data is sent to the superior system according to the IEEE C37.118 communication protocol.
What does RoCof stand for?
RoCoF is the time derivative of the power system frequency (df/dt). A large Rate of change of frequency can endager system operation and get more and more attention amongst system operators due to the rising existence of distributed energy resources.
What are WAMS in smart grids?
Nationwide networks of time-synchronized phasor measurement units (PMUs) are called Wide Area Monitoring Systems (WAMS). They allow users to centrally visualize and monitor phasors, detect islands, resynchronization and black start detection, grid stability and voltage monitoring. Furthermore, using interfaces allows the passing of results to SCADA.
What is a Power Quality Spreading & Mitigation Analysis?
Mitigation from EV charging stations or heat pumps result in a shift of emissions to higher-frequent areas. Using synchronous measurements of a multitude of input channels and instruments via GPS allow the analysis of the whole system.
– Closing the Q&A
Summing up all the previous chapters of our power quality series, we think you deserve a well-deserved break. Following this article you will find an opportunity to get a fresh perspective in your working day. From now on we can finally take more deep dives into PQ areas that are really interesting..