Types of faults in photovoltaic modules 2
- Posted by Andre
- On 22. January 2024
- 0 Comments
- Hot Spot, PV faults
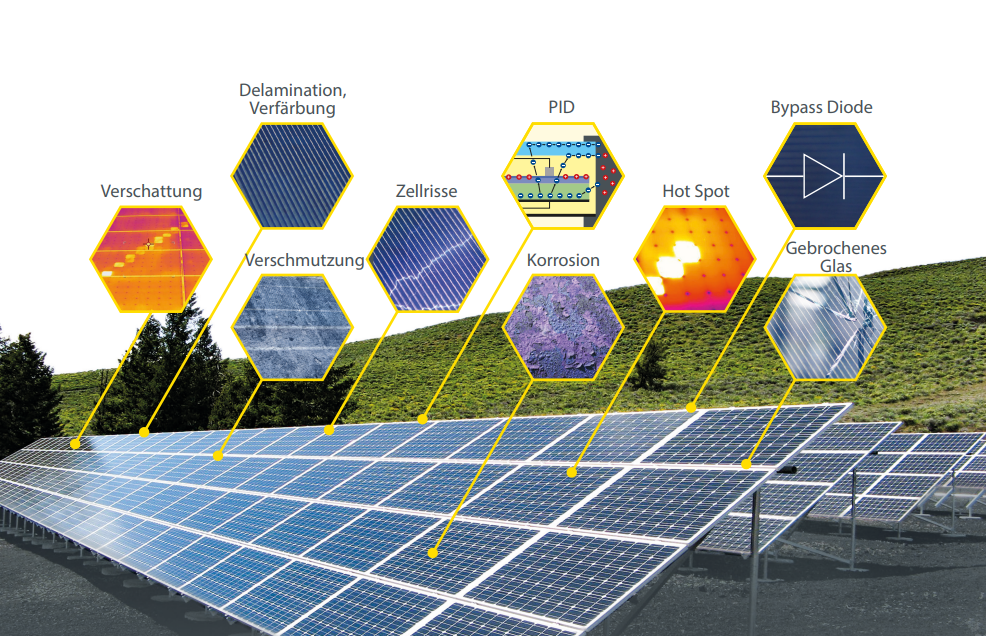
The 2nd edition of the blog post “Types of faults in photovoltaic modules” is coming late but still. This time it’s all about hot spots. If you have any further questions on the topics, we will be happy to provide you with further information.
Table of Contents
Hot Spots

Understanding HotSpots
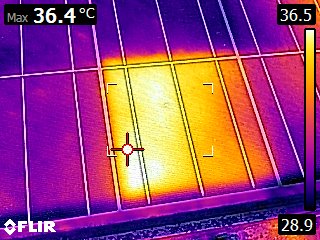
Hot Spots refer to localized areas of elevated temperature within a photovoltaic module. These hotspots can occur for various reasons, and if left unaddressed, they can lead to decreased efficiency, reduced power output, and even long-term damage to the solar panels.
Causes of HotSpots
Partial Shading: When certain parts of a solar panel receive less sunlight due to shading from nearby objects, such as trees or buildings, the shaded cells may become a hotspot. This is because the shaded cells can act as resistors, causing an increase in temperature.
Mismatched Cells: Manufacturing variations or mismatched cells within a module can result in uneven power production. Cells with lower efficiency may generate less electricity, causing them to heat up and create hotspots.
Cell Defects: Manufacturing defects or damage during transportation and installation can lead to cell malfunctions. A malfunctioning cell can become a hotspot as it fails to contribute its fair share to the overall energy production.
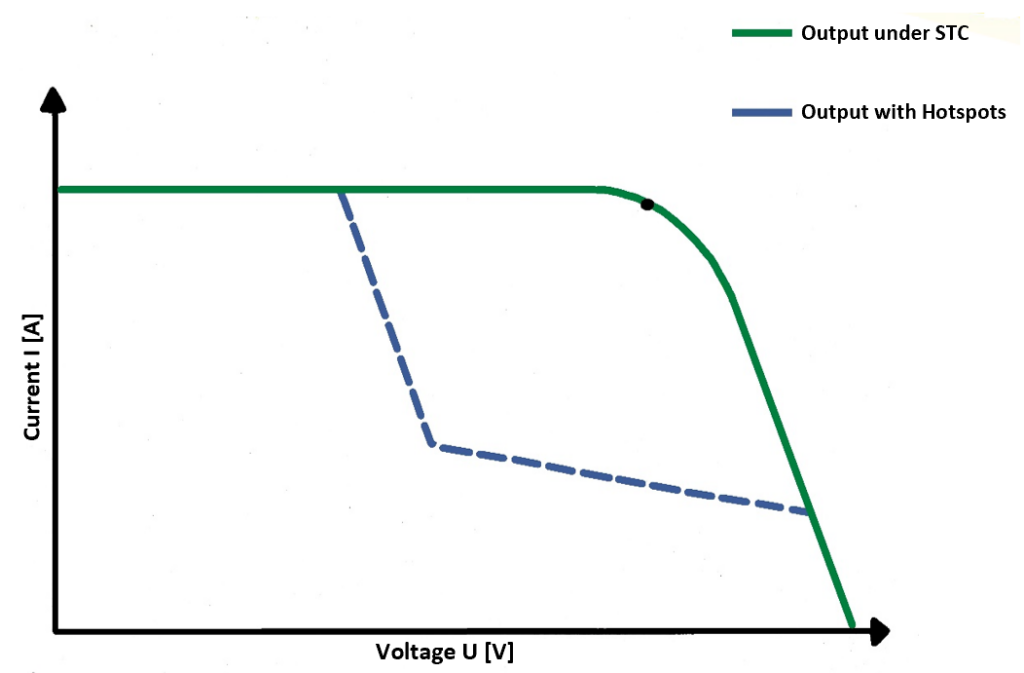
This image shows a possible variant of a string or module with a Hot Spot problem. It can be seen that both the open-circuit voltage and the short-circuit current are not reduced. However, the MPP is considerably lower than without the hot spot. The area between the two curves describes the lost power.
Effects of Hot Spots
Reduced Efficiency: Hot Spots can significantly reduce the overall efficiency of a photovoltaic module. The elevated temperatures hinder the performance of solar cells, leading to a decrease in power output.
Decreased Lifespan: Prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures can accelerate the aging process of solar cells, shortening the lifespan of the entire photovoltaic module.
Safety Concerns: Hot Spots can pose safety risks, as excessively high temperatures may result in thermal runaway, where the module experiences a rapid increase in temperature, potentially leading to fire hazards.
Mitigating Hot Spots
Bypass Diodes: Photovoltaic modules are equipped with bypass diodes that help mitigate the impact of shading. These diodes redirect the current flow, preventing hotspots in shaded areas.
Regular Maintenance: Periodic inspection and maintenance of solar panels can identify and address issues such as soiling, damage, or defects before they escalate into Hot Spots.
PV Master 10 for photovoltaic inspection
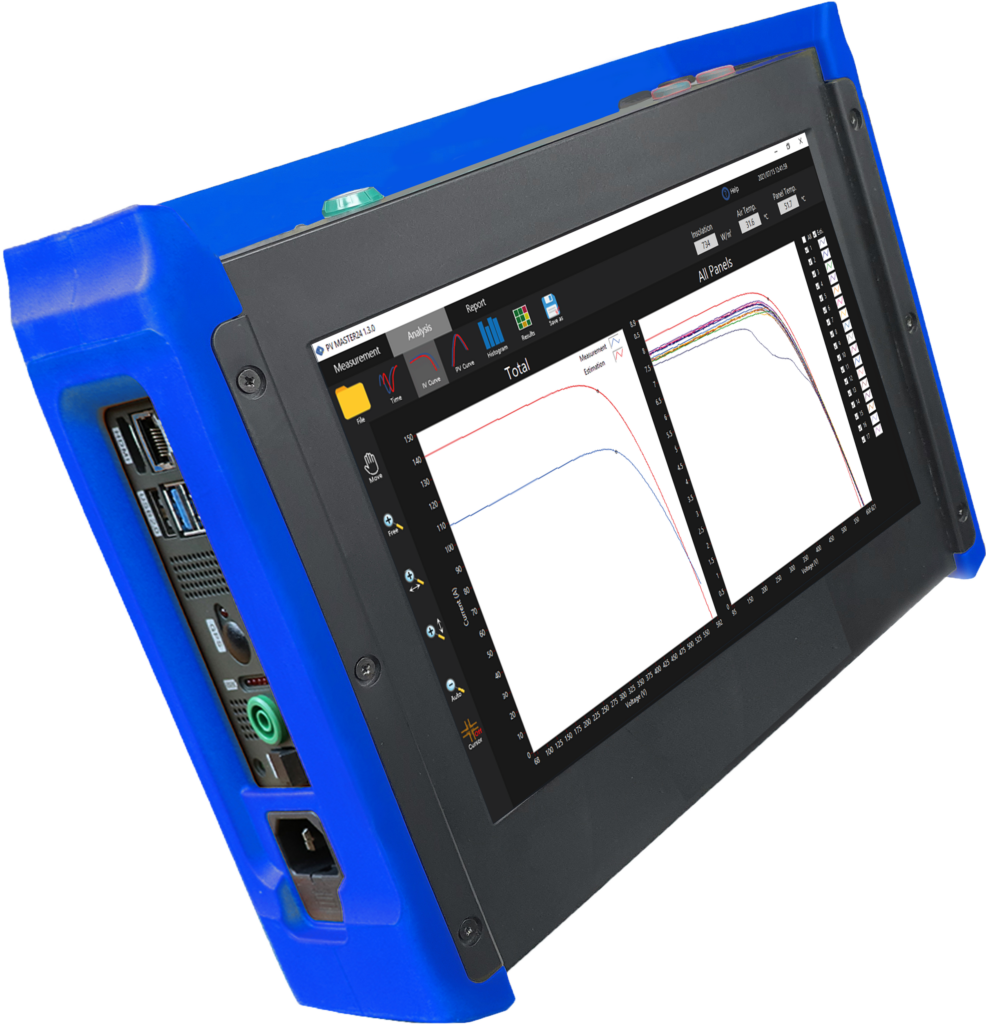

The PV Master 10 employs advanced Time-Sync Technology to measure up to 20 channels or strings simultaneously (1 channel intern / up to 20 channels with extension box). It offers precise potential measurement up to 1600V and IV-curve tracing capabilities at the same potential level. With a capacity of up to 30 A, it ensures accurate measurements. Additionally, there are two inputs available for thermocouples (Type K) and one for irradiance measurement via BNC. The device boasts a battery pack that ensures up to 4 hours of continuous operation, complemented by an 11-inch multi-touch full HD display for enhanced usability. Notably, it can detect serial and parallel mismatch losses, making it a comprehensive tool for efficient analysis in the field.
Wrapping up
Where can I get more information?


